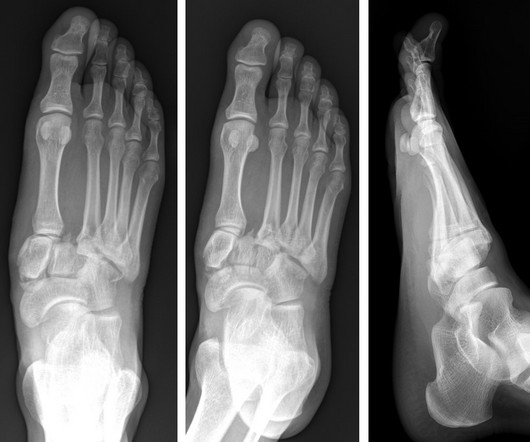
Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation
Global Radiology CME
NOVEMBER 10, 2023
A) AP radiograph of Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation demonstrates the circled “fleck sign” or Lisfranc ligament avulsion fracture fragment. (B) C) The lateral radiograph notes with a circle, the dorsal sub dislocation of the metatarsal base. Radiographs should be repeated after two weeks to ensure surgery is unnecessary.








Let's personalize your content